Have you ever looked up at the sky at night? Ancient books tell us that humans have been doing this for thousands of years. Some people have spent all their lives studying the stars in the night sky. Poems have been written telling us of their beauty if you live in the city you may wonder what all the fuss in about. Why do people become so curious about the stars?
If you ever away from city lights, on a cloudless night, and with no moon, you can begin to see why. Now there are a thousand more stars than you ever see from the city. If you watch for a long time you see they appear to move slowly across the sky. Maybe you will see a meteor streak across the inky blackness. Meteors are sometimes wrongly called 'falling stars' or 'shooting stars'. But what are stars? What are meteors?
 |
| a telescope sees many more stars than we can with the naked eye. |
The Night Sky
The stars you can see on a dark night look such a jumble that you may wonder if we can ever understand them.
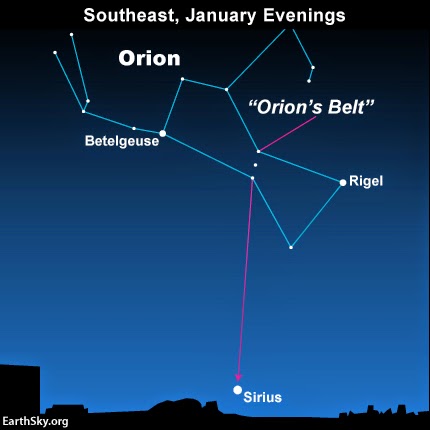 |
| Orion position at southeast |
Constellations
At night, the Moon is easy to see and watch. If you are away from city lights, the only other easy thing to pick out may be the Milky Way. It is like a white band across the night sky. If we look closer, we may see that some stars are much brighter than others. Ancient astronomers, people who study the stars, saw that these bright stars were in groups. They saw that the same groups of stars appeared to move across the sky each night. They always rose above the horizon somewhere in the east, and went down (set) over the western horizon. These groups of stars are now called constellations.
 |
| Constellation of Orion |
 |
| The Saucepan of Orion |
Astronomers looking at Orion at, say, 8 o'clock each night, saw that its shape was always about the same. But its place in the sky changed as the night went on. if they looked at Orion at 8 o'clock on, say, the 15th day of each month for a whole year, then they saw that its position in the sky changed a little as the year passed. The other constellations and stars moved in the same way.
 |
| The Southern Cross and Pointer |
The Zodiac
The Moon is easy to see in the night sky. Like Orion, it 'rises' in the east moves across the sky and 'sets' in the west. in fact, it follows the same path across the sky that the Sun took during the daylight hours. The path taken by the Sun and Moon across the sky is called the ecliptic.
As the Moon moves across the night sky, it passes in front of some constellations-12 in total over the whole year. Many of these constellations are named after animals. For this reason, ancient astronomers called them the zodiac, which means 'path of the animals'.
 |
| Position of Zodiac |
Only about half of the zodiac can be seen each evening. This is because the rest is below the horizon.
Early on a summer's evening it is quite low in the northern sky. But at the same time on a winter's evening the zodiac is nearly overhead. Like other constellations, those in the zodiac move east to west across the sky at night. As the year goes by, their place in the sky at any one time (say 4 a.m.) also changes like that of Orion.
~The World of Science
Book Two, Third Edition.
D.A. Heffernan & M.S. Learmonth
Longman
